The Basics of Health insurance is a vital component of healthcare in the United States. However, for many individuals, understanding how health insurance works can be challenging. Terms like premiums, deductibles, and co-pays are often encountered when navigating through insurance plans, and having a solid grasp of these concepts can help you make informed decisions regarding your healthcare and finances.
In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the basics of health insurance, explaining what premiums, deductibles, and co-pays are, how they affect your out-of-pocket costs, and how to evaluate them when selecting a plan. By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of how these elements influence your overall health insurance costs and your healthcare experience.
1. What Is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company that helps cover medical expenses. In exchange for regular payments (premiums), the insurer covers certain healthcare costs, which can include doctor visits, surgeries, medications, and hospital stays. The goal of health insurance is to minimize the financial burden of healthcare, offering a safety net when medical care is needed.
While health insurance helps reduce the cost of medical treatments, it doesn’t eliminate all out-of-pocket expenses. These additional expenses typically come in the form of premiums, deductibles, and co-pays. Let’s explore each of these terms in detail.
2. What Are Health Insurance Premiums Basics of Health ?
A premium is the amount of money you pay to your insurance provider in exchange for coverage. Typically, premiums are paid on a monthly basis, although some plans allow quarterly or annual payments. Your premium ensures that you stay enrolled in your health insurance plan.
How Premiums Work:
Your monthly premium is generally fixed and can vary based on several factors:
- Type of Plan: Plans with lower premiums, such as Bronze plans, may have higher deductibles and co-pays, while Platinum plans tend to have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Age: Older individuals typically pay higher premiums than younger individuals because they are at greater risk of requiring medical care.
- Location: Premiums can differ based on where you live because healthcare costs vary from region to region.
- Tobacco Use: Tobacco users often pay higher premiums, as smoking is associated with increased health risks.
- Family Size: If you are covering a spouse or children, your premium will be higher compared to an individual plan.
Although premiums ensure that your coverage remains active, they do not go toward covering your medical expenses directly. It’s essential to balance a premium you can afford with the potential out-of-pocket costs you might incur.
Key Takeaways:
- Premiums are paid regularly (usually monthly) and ensure that you maintain your insurance coverage.
- The amount of your premium depends on various factors, including the type of plan, your age, location, and tobacco use.
- Premiums don’t go toward out-of-pocket medical costs, but they keep your coverage active.
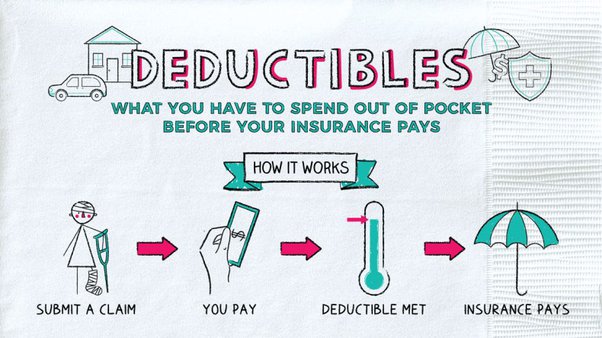
3. What Is a Deductible in Health Insurance?
A deductible is the amount of money you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance begins to share the cost. The deductible must be met before the insurer will cover most services, except for preventive care, Basics of Health which is often covered without having to meet the deductible.
How Deductibles Work:
For example, if your health insurance plan has a $2,500 deductible, you would need to pay the first $2,500 of your healthcare expenses. After meeting the deductible, your insurance begins to pay a larger portion of your medical bills.
Deductibles can vary from plan to plan, and some plans have separate deductibles for specific services, such as prescription drugs. Additionally, some services, such as preventive care (like vaccinations or routine screenings), may be covered before the deductible is met.
Deductibles are typically higher for plans with lower monthly premiums, and lower for plans with higher premiums. As a result, you must weigh the costs and benefits of selecting a plan with a higher deductible versus one with a lower deductible.
Key Takeaways:
- The deductible is the amount you need to pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts contributing to your healthcare costs.
- Preventive care may be covered without needing to meet your deductible, but most other services will require you to pay for them first.
- Higher deductible plans tend to have lower premiums, while lower deductible plans typically have higher premiums.
4. What Are Co-pays in Health Insurance?
A co-pay (or co-payment) is a fixed amount you pay for a healthcare service at the time of receiving it. Co-pays are separate from your deductible, and they don’t go toward meeting it. Co-pays can be required for various services such as doctor visits, emergency room trips, and prescription medications.
How Co-pays Work:
For example, if you visit your primary care physician, you may have a $20 co-pay, meaning you pay $20 for the visit, and the insurance covers the remaining cost. Similarly, a visit to a specialist might have a higher co-pay, such as $50. Emergency room visits often have much higher co-pays, sometimes up to $200 or more.
Co-pays can vary depending on the type of service, and they may be higher for certain services such as specialist visits or emergency care. Most health insurance plans include co-pays for prescriptions as well, with co-pays differing for generic drugs, brand-name drugs, and specialty medications.
Key Takeaways:
- Co-pays are fixed fees that you pay for certain healthcare services, such as doctor visits and prescriptions.
- Co-pays are due at the time of service, and they don’t count toward your deductible.
- The amount you pay as a co-pay varies depending on the type of healthcare service you receive.
5. How Premiums, Deductibles, and Co-pays Work Together Basics of Health
While premiums, deductibles, and co-pays are separate components of a health insurance plan, they work together to form your overall out-of-pocket healthcare costs. Here’s how these elements interact:
Scenario 1: High Deductible, Low Premium Plan
If you select a plan with a high deductible and low premium, you will pay lower monthly premiums but may need to pay a significant amount out-of-pocket before your insurance begins covering your healthcare expenses. For instance, if your deductible is $5,000, you will need to cover that amount before your insurer starts paying for services. However, your monthly premium is likely to be lower.
Once you meet your deductible, you will be responsible for co-pays, and your insurer will start paying a larger share of the costs. While this option may be more affordable in terms of premiums, it can result in higher costs if you need frequent medical care.
Scenario 2: Low Deductible, High Premium Plan
In contrast, a plan with a low deductible and high premium means you’ll pay more each month but won’t have to pay as much out-of-pocket for services before your insurance begins contributing. If your deductible is $1,000, you’ll only need to pay that amount before your insurance starts covering your expenses. In addition, co-pays for doctor visits or prescriptions may be lower.
This option can be beneficial if you expect to use healthcare services more frequently, as it reduces your out-of-pocket costs. However, the higher premiums may not be ideal for individuals who rarely visit the doctor or need minimal healthcare services.
Scenario 3: Co-pays on Top of Deductibles
It’s important to remember that co-pays apply on top of your deductible. For example, even if you’ve met your $3,000 deductible, you may still have to pay a $20 co-pay for each doctor’s visit or a $50 co-pay for specialist visits. Co-pays are a way for insurers to share the cost of healthcare services, and they are typically required when you visit a doctor, get a prescription, or use emergency services.
Key Takeaways:
- Premiums determine your monthly cost, deductibles dictate how much you pay before insurance starts contributing, and co-pays apply per service.
- Higher deductible plans often have lower premiums, while lower deductible plans tend to have higher premiums.
- Co-pays are separate from your deductible and are required for certain services, even after you meet your deductible.
6. How to Choose the Right Health Insurance Plan for You Basics of Health
When selecting a health insurance plan, it’s important to consider how the premiums, deductibles, and co-pays fit into your overall healthcare needs and financial situation. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- How often do you visit the doctor? If you see doctors frequently or have ongoing medical needs, you may prefer a plan with a lower deductible and lower co-pays, even if it means paying a higher premium.
- What are your healthcare needs? If you need regular prescriptions or have a chronic condition, it’s worth considering a plan with lower co-pays for medications and services.
- What can you afford? Consider your budget when choosing a plan. While lower premiums may seem appealing, they can result in higher out-of-pocket costs if you need a lot of care. Similarly, higher premiums can be more affordable for those who use healthcare services regularly.
It’s always a good idea to compare different plans, estimate your medical costs, and choose the one that aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation.
7. Conclusion
Understanding the basics of health insurance is essential for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. Premiums, deductibles, and co-pays are the key elements that define how much you’ll pay for your health insurance and the healthcare services you use. By knowing how these components work together, you can evaluate different plans and choose the one that best meets your needs, whether that means a plan with lower premiums or one that offers more comprehensive coverage with higher out-of-pocket costs.
Ultimately, understanding how premiums, deductibles, and co-pays affect your healthcare costs empowers you to make smarter decisions about your health insurance, ensuring that you get the coverage you need without breaking your budget.