Families Health insurance is one of the most important investments a family can make to protect the health and well-being of its members. Whether you’re navigating the options as a new parent or considering how to adjust coverage as your family grows, understanding health insurance for families is key to ensuring everyone stays healthy and financially protected.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover everything you need to know about health insurance for families, from choosing the right plan to understanding coverage options, managing costs, and maximizing benefits. Whether you’re new to health insurance or looking to optimize your existing coverage, this blog provides valuable tips to guide you through the process.
1. Why Health Insurance for Families Is Essential
Health insurance provides peace of mind by helping you manage the costs of medical care. Without insurance, a single medical emergency, chronic condition, or even routine medical care can result in significant financial strain. Health insurance helps protect you and your family from unexpected healthcare costs, ensuring that you can access necessary care without overwhelming financial burden.
For families, health insurance is particularly important because children may require a range of medical services, from routine checkups and vaccinations to emergency treatments and specialist care. Additionally, parents may need coverage for their own health needs, such as maternity care, chronic conditions, or preventive services.
With the right health insurance plan, your family can have access to preventive care, prescription medications, hospital stays, emergency services, mental health care, and more.
2. Types of Health Insurance for Families
There are several types of health insurance plans available to families, depending on your circumstances, employment status, and preferences. The primary options include employer-sponsored insurance, Marketplace plans, and government programs like Medicaid and CHIP.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Many families receive health insurance through an employer-sponsored plan, where the employer helps cover a portion of the premium cost. These plans typically provide comprehensive coverage and can be a more affordable option for families, especially if the employer contributes significantly to the premium.
- Cost-sharing: Employers often share the cost of premiums with employees, which can make the overall cost lower than purchasing a plan individually.
- Plan options: Employers usually offer several plans with different levels of coverage, which may include health maintenance organizations (HMO), preferred provider organizations (PPO), or exclusive provider organizations (EPO).
- Dependents: Employer-sponsored health insurance usually extends to spouses and children, so the whole family can be covered under one plan.
Marketplace Health Insurance (ACA Plans)
If you’re self-employed or don’t have access to employer-sponsored insurance, you can purchase health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace (also known as the Exchange), which was established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The Marketplace allows families to shop for plans based on their needs and budget.
- Coverage: Marketplace plans offer a range of coverage options, including Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum tiers. Bronze plans have the lowest premiums but higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs, while Platinum plans have higher premiums but lower deductibles and co-pays.
- Financial assistance: Depending on your income, you may qualify for subsidies to reduce the cost of premiums, deductibles, and co-pays.
- Open Enrollment: You can purchase Marketplace insurance during open enrollment, which typically occurs once a year, although special enrollment periods exist for certain life events like marriage, having a baby, or losing other coverage.
Medicaid and CHIP
For families with low income, Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) are two vital programs that provide free or low-cost coverage to children and adults. Eligibility varies by state, but these programs are available to families who meet certain income requirements.
- Medicaid: Medicaid provides coverage for low-income adults, pregnant women, and people with disabilities. It covers a wide range of health services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and long-term care.
- CHIP: CHIP provides coverage to children whose families earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private health insurance. CHIP offers low-cost or free coverage depending on income.
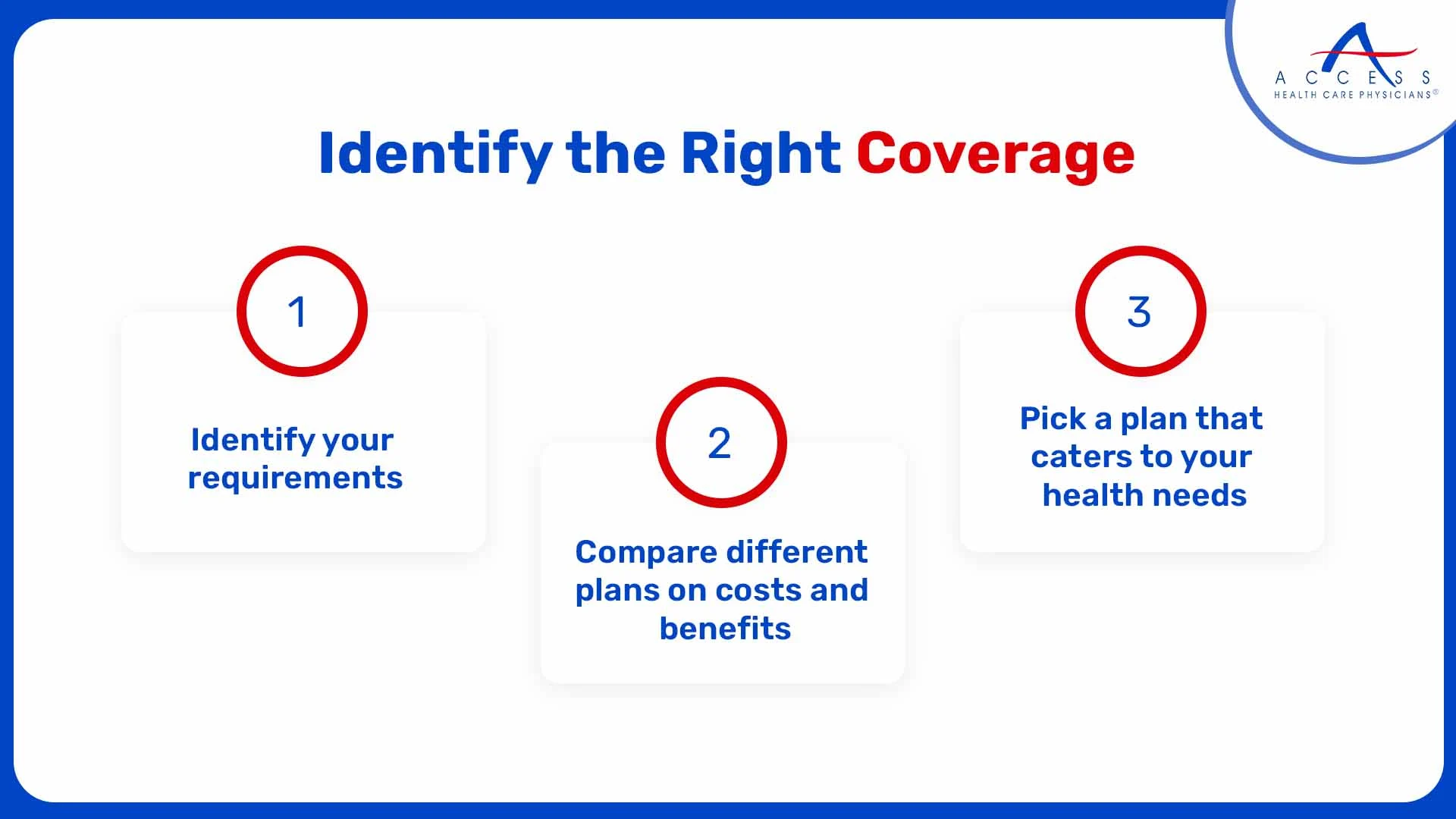
3. Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Health Insurance for Your Family
Choosing the right health insurance plan for your family involves evaluating various factors that can affect both your coverage and costs. Here are some critical things to consider:
Coverage Needs
Start by evaluating your family’s healthcare needs. Consider the following:
- Children’s needs: Does your child require regular doctor visits, vaccines, or specialist care? Are there any chronic conditions that require frequent care?
- Maternity and newborn care: If you’re planning a pregnancy or recently gave birth, look for plans that offer maternity care, prenatal visits, and newborn coverage.
- Chronic conditions: If any family member has a chronic illness or ongoing medical needs, ensure that the plan covers the necessary medications, specialists, and treatments.
- Mental health services: Mental health care is an essential part of overall well-being. Look for plans that provide adequate coverage for therapy, counseling, and psychiatric care.
Premiums and Deductibles
The premium is the monthly cost of the plan, but it’s not the only cost you should be concerned about. The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance starts covering your expenses. Understanding these costs is key to choosing an affordable plan.
- Premiums: Higher premiums usually result in lower out-of-pocket costs when you receive care. Look for a balance between affordable premiums and sufficient coverage.
- Deductibles: A lower deductible can be advantageous if you expect to need frequent medical care, but it may come with higher premiums. If you’re generally healthy and don’t expect to see the doctor often, a higher deductible plan may save you money in premiums.
Co-pays, Co-insurance, and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
In addition to premiums and deductibles, you’ll need to account for co-pays and co-insurance, which are the portions of the medical costs that you’re responsible for after your deductible is met.
- Co-pays: A co-payment is a fixed amount you pay for specific services, like doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Co-insurance: Co-insurance is a percentage of the total cost of a service that you pay after your deductible is met.
- Out-of-pocket maximum: This is the highest amount you will have to pay for covered services in a plan year. Once you reach this limit, the insurance company covers 100% of your medical costs.
Provider Network
Most health insurance plans have a network of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers. When selecting a plan, ensure that your family’s primary care physician and specialists are in-network, as out-of-network care may be more expensive.
- HMO vs. PPO: HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) plans require you to get care from in-network providers, and you often need a referral from your primary care physician to see a specialist. PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) plans offer more flexibility, allowing you to see any provider, but at a higher cost for out-of-network care.
- Out-of-network coverage: Some plans offer out-of-network coverage but at a higher cost. Be sure to check the details of your plan’s network.
Prescription Drug Coverage
If anyone in your family takes prescription medications, ensure that the health plan covers the drugs you need. Most plans have a formulary, or list of covered drugs, which can vary significantly from one plan to another.
- Generic vs. brand-name drugs: Some plans may cover only generic medications, while others offer coverage for brand-name drugs. Understanding the formulary is essential to avoid paying higher out-of-pocket costs for medications.
4. Tips for Managing Health Insurance Costs for Families
Health insurance for families can be costly, but there are several ways to manage these expenses effectively:
Use Preventive Care
Many health insurance plans cover preventive care at no cost to you. This includes routine checkups, vaccinations, screenings, and other services that can help catch health issues early and prevent more serious conditions from developing. Taking advantage of preventive services can save your family money in the long run by avoiding more costly medical treatments.
Maximize the Use of Your HSA or FSA
Health savings accounts (HSAs) and flexible spending accounts (FSAs) allow you to set aside pre-tax money to pay for qualified medical expenses, such as prescriptions, co-pays, and deductibles. These accounts can help reduce your taxable income while saving you money on out-of-pocket healthcare costs.
Shop Around for Prescription Medications
Prescription drug costs can be a significant portion of your healthcare expenses. To save money, consider using generic medications, shopping around for the best prices, or using discount programs. Some insurance plans also offer discounts through their pharmacies or online prescription services.
Take Advantage of Family Coverage
Most health insurance plans offer family coverage, which typically costs less than purchasing individual plans for each family member. Even if one or two members of your family are relatively healthy, the cost savings of family coverage can be significant, and it ensures that everyone is covered in the event of a health emergency.
Use Telemedicine Services
Many insurance plans now offer access to telemedicine services, allowing you to consult with healthcare providers via phone or video chat. Telemedicine can be a more affordable option for non-emergency medical consultations, such as mental health counseling or follow-up appointments.
5. Conclusion
Health insurance for families is an essential aspect of protecting your loved ones and ensuring that everyone receives the care they need. With so many options available, including employer-sponsored insurance, Marketplace plans, and government programs like Medicaid and CHIP, there are opportunities for families of all incomes to secure coverage.
By understanding the types of coverage, carefully evaluating your family’s healthcare needs, and managing costs through strategies like preventive care and HSAs, you can maximize the benefits of your health insurance plan while keeping your expenses under control.
Whether you’re choosing a new plan or looking to optimize your current coverage, this guide should give you the tools you need to make an informed decision and ensure that your family is fully covered in the event of illness or injury.